Data Storage
Definition
Data storage refers to the process of saving data onto a storage medium or device (digitalized data).
Introduction
Research data is valuable and should be stored securely to prevent loss and unauthorized access. Secure data storage is a crucial component of research data managementResearch data management is aimed at handling research data in a responsible and well-considered manner. The idea is to carefully organize, maintain and process research data using specific measures and strategies. The goal is to store data long-term and make it accessible and reusable by others, in line with good scientific practice. This enables easier verification of scientific findings, secures evidence, and allows for further evaluations and analyses of the data. Read More and a fundamental requirement for good scientific workGood scientific practice (GSP) represents a standardized code of conduct established in the guidelines of the German Research Foundation (DFG). These guidelines emphasize the ethical obligation of every researcher to act responsibly, honestly, and respectfully, also in order to strengthen public trust in research and science. They serve as a framework for guiding scientific work processes. Read More.
When working in research teams where multiple individuals access a shared data pool, it is essential to develop a data storage and security strategy early on. This strategy should address storage capacity, storage locations and media, access permissions (data protectionData protection includes measures against the unlawful collection, storage, sharing, and reuse of personal data. It is based on the right of individuals to self-determination regarding the handling of their data and is anchored in the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Federal Data Protection Act (Bundesdatenschutzgesetz), and the corresponding laws of the federal states. A violation of data protection regulations can lead to criminal consequences. Read More regulations), and protection against data loss. Implementing various security measures and backupThe term backup means data protection or data recovery and refers to the copying of data as a precaution in the event that data is lost, e.g. due to hard drive damage or accidental deletion. The data can be restored with a backup. For this purpose, the data record is additionally saved on another data carrier (backup copy) and stored offline or online. Read More routines can help minimize the risk of losing data.
Different storage locations and media offer various advantages and disadvantages in terms of compatibility, mobility, access, security, durability, backup options, and encryption methods, as outlined below (Baur, 2021; Forschungsdaten.info, 2023g).
Source: Overview of different storage locations and media, Anne Voigt, 2023, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Motivation
Research data is unique and valuable and should be securely stored and protected to prevent the loss of one's research work. Possible data losses can have a variety of human or technical causes, such as accidental overwriting or deletion, hacker and Trojan attacks, or loss of access credentials to a storage location. Storage media are not always reliable and can break, be lost, or be stolen. Additionally, software and hardware may become incompatible over time due to technological advancements.
Mobile and flexible working is an integral part of the research and professional world. This requires time- and location-independent access to data. Depending on the situation, such as working in the field without internet access versus analyzing data in an office, different requirements for storage locations and media apply. Therefore, it is important to consider early on which measures and regular routines should be established to protect research data from loss.
Methods
In addition to selecting the appropriate storage location for research data, regularly creating backup copies of original files and archiving them (so called backup routines) plays a crucial role. BackupThe term backup means data protection or data recovery and refers to the copying of data as a precaution in the event that data is lost, e.g. due to hard drive damage or accidental deletion. The data can be restored with a backup. For this purpose, the data record is additionally saved on another data carrier (backup copy) and stored offline or online. Read More files should always be stored on a different medium and separately from the original data. After performing a backup, it is advisable to check the data for accuracy and completeness.
The 3-2-1 rule has proven to be an optimal backup strategy:
- 3: Create three copies of the data (the original plus two backups).
- 2: Store the copies on two different storage technologies (e.g., internal hard drive and network drive).
- 1: Keep one copy externally (at a different physical location, such as in the cloud).
Many universities offer backup services and routines, which are mostly automated. However, access to these services is usually lost upon leaving the institution.
Therefore, researchers should always develop their own well-planned backup strategies to protect their data. The following questions can be helpful:
- What exactly should be backed up, and how often?
- Should a backup be created for all data or only specific parts?
- On which systems should backups be stored?
- What is the primary system for original files, and which systems will be used for backups?
- Is quick access to the data important?
- How frequently should backups be performed?
Practical Examples
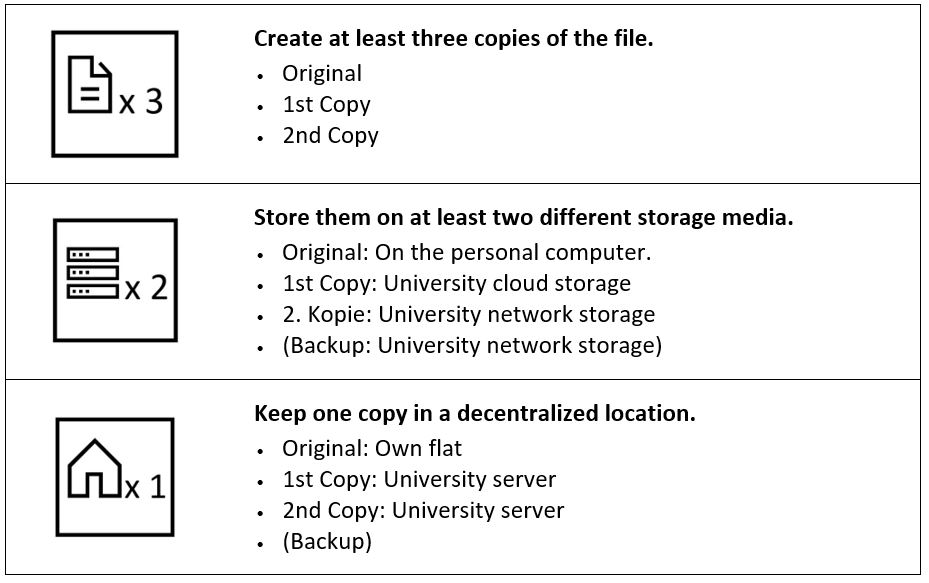
Source: Example of the 3-2-1 rule, Anne Voigt, 2023, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Literature and References
Baur, J. (2021). FDM erklärt – Forschungsdatenspeicherung. Forschungsdaten – Aktuelles & Wissenswertes. Blog der RWTH AAchen University. https://blog.rwth-aachen.de/forschungsdaten/2021/08/20/fdm-erklaert-forschungsdatenspeicherung/
Forschungsdaten.info. (2023g). Datenspeicherung und die Lebensdauer von Datenträgern. forschungsdaten.info. https://forschungsdaten.info/themen/speichern-und-rechnen/datenspeicherung-und-die-lebensdauer-von-datentraegern/
Citation
Voigt, A. & Dührsen, J. L. (2023). Data Storage. In Data Affairs. Data Management in Ethnographic Research. SFB 1171 and Center for Digital Systems, Freie Universität Berlin. https://en.data-affairs.affective-societies.de/article/datastorage/
