Folder Structure
Definition
The term folder structure (also known as a directory tree or directory structure) refers, “in the strict sense, to the hierarchical layout of the entire file system on an individual computer, and in a broader sense, to a directory service for various objects (such as users, devices, services, file shares, and packages) within a company network. A tree structure is commonly used, starting with a root and branching out as needed” (Wikipedia, 2023).
Introduction
Folders are fundamental components of a directory structure and help users manage files clearly. Files are typically organized thematically and stored in folders whose names reflect their content. The folder structure is displayed as a directory tree. At each level, folders can contain subfolders and/or files. This creates a hierarchical folder structure (tree structure) that ideally provides a clear overview of the data.
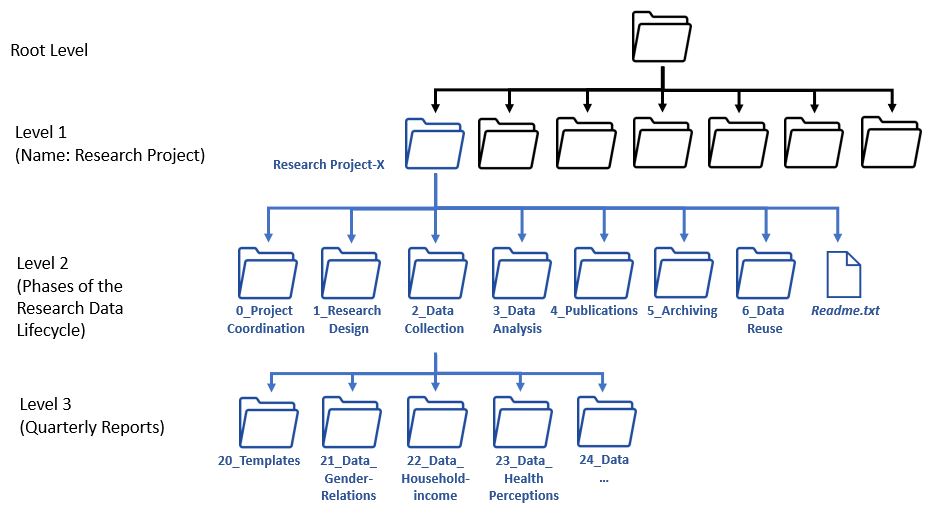
Source: Example Folder Structure, Anne Voigt, 2023, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Each element (file or folder) has a unique path ("address"), displayed in the browser, indicating where a file is located and how to reach it from the root.
Example: C:\Documents\Sem1\Module1\2012-02-10_M01_Lecture1.pdf
Motivation
A structured, effective folder system is a key element of file storage and security – not only for individual work but especially for project teams. In larger teams, vast amounts of information and materials accumulate. Project teams face the challenge of organizing and providing access to diverse materials, often in multiple versions, so they remain identifiable, searchable, and accessible to all team members.
A clear, comprehensible folder structure:
- Follows a consistent schema with a logical, hierarchical structure.
- Is transparent (even for outsiders and future use): easy data retrieval through clear and precise naming.
- Is organized: only as many folders per level as can be viewed at a glance.
- Supports quick data access and reduces search times.
- Facilitates the continued processing and reuse of data.
- Reduces the risk of data loss due to accidental deletion or overwriting.
Methods
General Tips for Creating an Effective Folder Structure:
- Avoid building the structure spontaneously; plan a systematic approach.
(In project teams: collaboratively develop a structure that can be used across platforms.) - For clarity: consider adding a README fileReadMe files in the context of systems or projects contain information about the respective system, project, etc., to help users orient themselves. Read More at the top-level folder with guidelines on file organization.
- Build a hierarchical structure: from general to specific.
- Top-Level: Ideally, the structure ensures a document is stored in only one folder.
- Use content-related folder names (keep names short, concise, and descriptive).
- If a document needs to be stored in multiple locations, use shortcuts/links (at both folder and file levels).
- Avoid excessive nesting: optimally, folder structures should be no more than three levels deep. (The fewer layers, the easier it is for visual memory to navigate.)
The “7-Folder System“ widely used in corporate settings (Sekretaria, 2023):
- First Level: Maximum of 7 folders
- Second Level: Maximum of 7 folders per folder (7 × 7 = 49)
- Third Level: Maximum of 7 folders per folder (7 × 7 × 7 = 343)
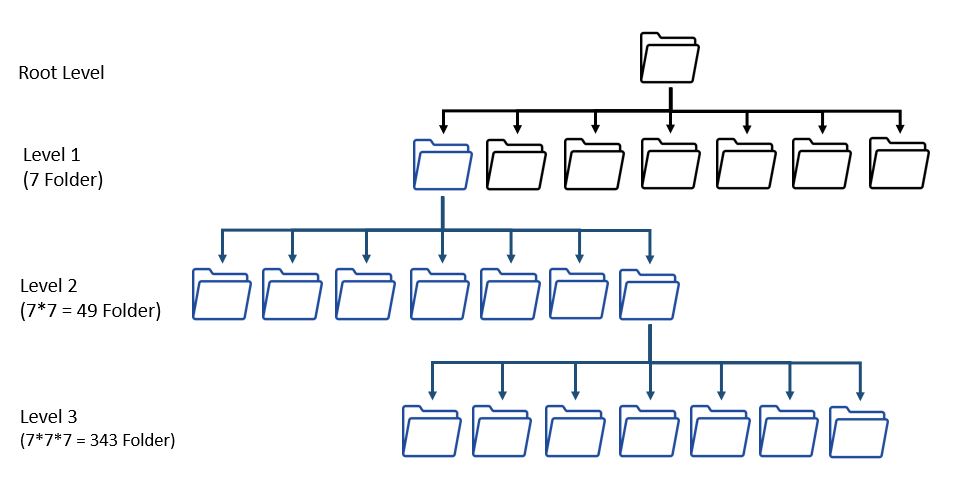
Source: 7-Folder System, Anne Voigt, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Folder Structure in Projects
Helpful categories for structuring folders in projects include (VerbundFDB, 2023):
- Work packages or functional units within a project
- Dates or timeframes (e.g., months, quarters, years)
- Folder content or types (e.g., research data, publications/reports, data analyses, conferences, literature, project coordination)
- File types (formatsThe terms 'file type' and 'file format' are often used interchangeably. A distinction is made between proprietary and open file formats. Proprietary formats usually require fee-based software to access, as they may not be compatible with other programs (e.g., PowerPoint for .ppt files or Photoshop for .psd files). In contrast, open formats such as .rtf or .png are based on standards and can be opened by many programs. Read More)
- Depending on context, personal initials or identifiers
Folder Sorting
To maintain consistent folder order, add a number prefix indicating its position in the hierarchy:
- First Level: Prefix 0_ bis 9_
- Second Level: Prefix 00_ bis 99_
- Third Level: Prefix 000_ bis 999_
- Fourth Level: Prefix 000-0_ bis 999-9_ (use a hyphen to avoid confusion with year numbers)
- Third Level: Prefix 000_ bis 999_
- Second Level: Prefix 00_ bis 99_
Practical Examples
Examples

Source: Folder Structure of a Research Project, Anne Voigt, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Literature and References
Sekretaria (2023). Ablage im Griff mit dem 7-Ordner-System. Sekretaria. https://www.sekretaria.de/bueroorganisation/organisation/ablage/7-ordner-system/
Verbund Forschungsdaten Bildung. (FDB, 2018). Dateien benennen und organisieren. fdb. https://www.forschungsdaten-bildung.de/dateien-benennen
Wikipedia. (2023). Verzeichnisstruktur. Wikipedia. https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Verzeichnisstruktur
Citation
Voigt, A. (2023). Folder Structure. In Data Affairs. Data Management in Ethnographic Research. SFB 1171 and Center for Digital Systems, Freie Universität Berlin. https://en.data-affairs.affective-societies.de/article/folder-structure/
